IMO K10S1, K30S, K60
The following format applies to all K series PLCs (Including the K7)
Details on the device address can be found in the Device Properties Information Topic.
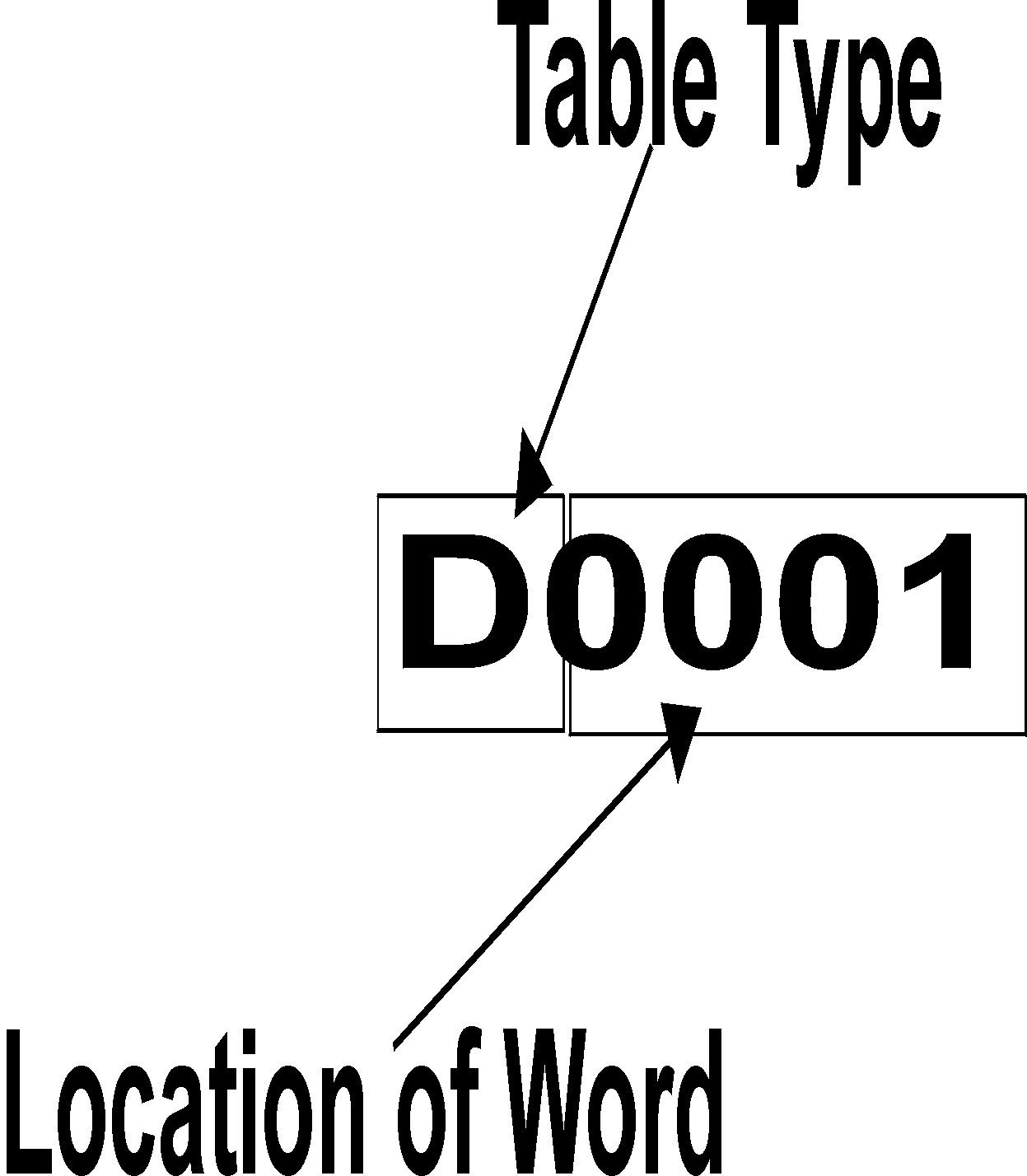
External Address Format
The External Address is an ascii string which exactly references an item of data within the PLC. It can be entered at configure time as a text string, and will be validated by the system before use. For this protocol the external address has the following format:
N - dec number 0 - 9
H - Hex number 0 - F
|
Addressing Bits |
Addressing Words | |||
|
Type |
Location |
Offset |
Type |
Location |
|
M |
NNN |
H |
D |
NNNN |
|
P |
NNN |
H |
T |
NNNN |
|
K |
NNN |
H |
C |
NNNN |
|
L |
NNN |
H |
|
|
|
F |
NNN |
H |
|
|
|
X |
NNN |
H |
|
|
|
Y |
NNN |
H |
|
|
Offset Format
The software also allows an item of data within the PLC to be referenced by means of a table selection and an offset. The following tables show the offset and table formats for the different PLC types:
PLC Tables K10S1
|
Table |
External Address Type |
Type |
Offset Format |
Offset Range |
Privilege R = Read W = Write |
Description |
|
M |
M |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-015F |
RW |
Auxiliary relay |
|
P inputs |
P |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-0007 |
R |
Physical inputs |
|
P outputs |
P |
Bit |
NNNH |
0010-0015 |
RW |
Physical outputs |
|
K |
K |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-007F |
RW |
Keep relay |
|
L |
L |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-007F |
RW |
Link relay |
|
F |
F |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-015F |
R |
Special relay |
|
C0 |
X |
Bit |
NNN |
000-015 |
R |
Contact bits for counters |
|
T0 |
Y |
Bit |
NNN |
032-047 |
R |
Contact bits for timers |
|
D |
D |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0063 |
RW |
Data register |
|
T |
T |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0047 |
RW |
Timers |
|
C |
C |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0015 |
RW |
Counters |
PLC Tables K30S
|
Table |
External Address Type |
Type |
Offset Format |
Offset Range |
Privilege R = Read W = Write |
Description |
|
M |
M |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-031F |
RW |
Auxiliary relay |
|
P |
P |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-002F |
RW |
Physical inputs and outputs |
|
K |
K |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-015F |
RW |
Keep relay |
|
L |
L |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-015F |
RW |
Link relay |
|
F |
F |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-015F |
R |
Special relay |
|
C0 |
X |
Bit |
NNN |
000-127 |
R |
Contact bits for counters |
|
T0 |
Y |
Bit |
NNN |
096-127 |
R |
Contact bits for timers |
|
D |
D |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0255 |
RW |
Data register |
|
T |
T |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0127 |
RW |
Timers |
|
C |
C |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0127 |
RW |
Counters |
PLC Tables K60S
|
Table |
External Address Type |
Type |
Offset Format |
Offset Range |
Privilege R = Read W = Write |
Description |
|
M |
M |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-031F |
RW |
Auxiliary relay |
|
P |
P |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-005F |
RW |
Physical inputs and outputs |
|
K |
K |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-015F |
RW |
Keep relay |
|
L |
L |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-015F |
RW |
Link relay |
|
F |
F |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-015F |
R |
Special relay |
|
C0 |
X |
Bit |
NNN |
000-127 |
R |
Contact bits for counters |
|
T0 |
Y |
Bit |
NNN |
096-127 |
R |
Contact bits for timers |
|
D |
D |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0255 |
RW |
Data register |
|
T |
T |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0127 |
RW |
Timers |
|
C |
C |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0127 |
RW |
Counters |
PLC Tables K7
|
Table |
External Address Type |
Type |
Offset Format |
Offset Range |
Privilege R = Read W = Write |
Description |
|
M |
M |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-191F |
RW |
Auxiliary relay |
|
P |
P |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-031F |
RW |
Physical inputs and outputs |
|
K |
K |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-031F |
RW |
Keep relay |
|
L |
L |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-063F |
RW |
Link relay |
|
F |
F |
Bit |
NNNH |
0000-063F |
R |
Special relay |
|
C0 |
X |
Bit |
NNN |
000-255 |
R |
Contact bits for counters |
|
T0 |
Y |
Bit |
NNN |
000-255 |
R |
Contact bits for timers |
|
D |
D |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-4999 |
RW |
Data register |
|
T |
T |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0255 |
RW |
Timers |
|
C |
C |
Word |
NNNN |
0000-0255 |
RW |
Counters |
Timers and Counters
The word tables C and T contain the PLC counters and timers respectively. The bit tables C0 (External address type X) and T0 (External address type Y) refer to the contact bits for counters and timers respectively. It should be noted that the hex bit offset component of the external address should always be configured as zero for these two bit tables. For this reason the offset format for these two bit tables is missing the hex digit component since it is redundant.
Property Pages
No property pages exist for this protocol
Protocol Compatibility
A bit type table such as ‘M’ or ‘P’ will support the configuration of point types bigger than a bit, but only up to 16 bit types. Types bigger than 16 bits cannot be configured. If a 16-bit point is configured for example, 16 bits will be read from the table to fill the point. Under RS485 a drive out to a multiple bit point will work, however under RS232 this is not supported and will cause a comms error. For K7, multiple bit driveouts are not supported on either RS485 or RS232. Single bit drive outs work in all cases.
A word type table such as ‘D’ supports the configuration of smaller or bigger point types. All larger point types will read the required number of words to fill the point. Byte type points will scale down the word to fit it into a byte. Bit type points allow the selection of a bit offset to reference the required bit from the word (0-15). In the case of bit selection points, drive outs will perform a read/modify/write operation as the protocol does not support a bit set operation in this case.
Port Settings
Port settings are configurable for all of the PLC’s within the PLC programming software. The following shows a typical port setup:
RS232/RS485 2 wire/RS485 4 wire
|
|
Baud Rate |
9600 |
|
|
Data Bits |
8 |
|
|
Stop Bits |
1.0 |
|
|
Parity |
None
|
Wiring Connections
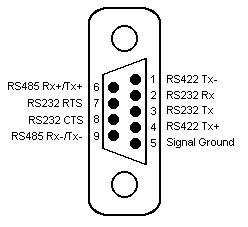
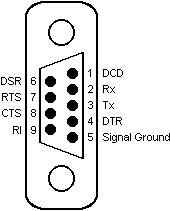
Connection of the PLC to a panel will be via either COM1 or COM2, using RS232, RS485 4 wire or RS485 2 wire communications. The panel pin out diagram is shown below:

Connection of the PLC to a PC running OPC Server will be via any available COM port, which may be either 25 pin or 9 pin depending on what is available. The PC will only support RS232 mode, an intelligent RS485-to-RS232 converter will be required to connect using RS485 2 wire or 4 wire communications. The COM port pin out is shown below:
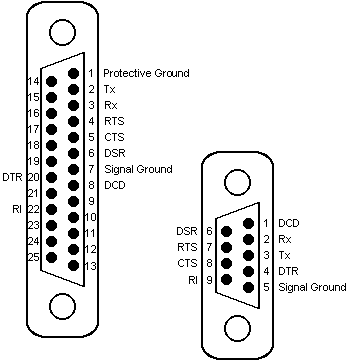
The IMO K30 and K60 PLCs have two methods of connection, either through the RS232 port on the PLC itself, or by connection to a comms module using RS485 2 wire or 4 wire communications. The RS232 port on the PLC has the following pin out:

The comms module has screw terminal connections for RS485 communications.
The following shows the correct wiring for connection to the IMO K30 or K60 PLC:



The IMO K10S1 PLC has two methods of connection, either through the RS232 port on the PLC, or by 2 wire RS485 connection using the screw terminals. The RS232 connection uses a supplied lead (KLC-010) with a 9 pin d-type connector one end, and a PS/2 connector which plugs into the PLC. The wiring diagram for this cable is not shown here.
The following shows the correct wiring for connection to the IMO K10S1 PLC using 2 wire communications:

The IMO K7 PLC has two methods of connection, either through the RS232 port on the CPU module, or by connection to a comms module using RS232, RS485 2 wire or 4 wire communications. The RS232 port on the CPU module has the following pin out:
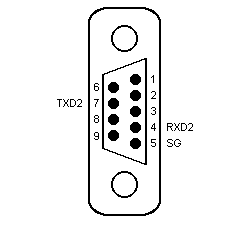
An RS232 comms module has a standard pin out as follows:
An RS485 comms module has screw terminal connections for RS485 communications.
The following shows the correct wiring for connection to an IMO K7 series PLC through the CPU module:

The following shows the correct wiring for connection to an IMO K7 series PLC through a comms module:



Examples
Addressing a bit in the M table
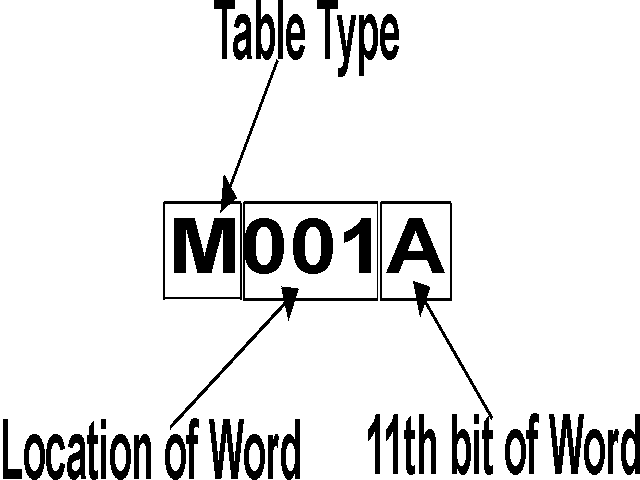
Addressing a word in the D table